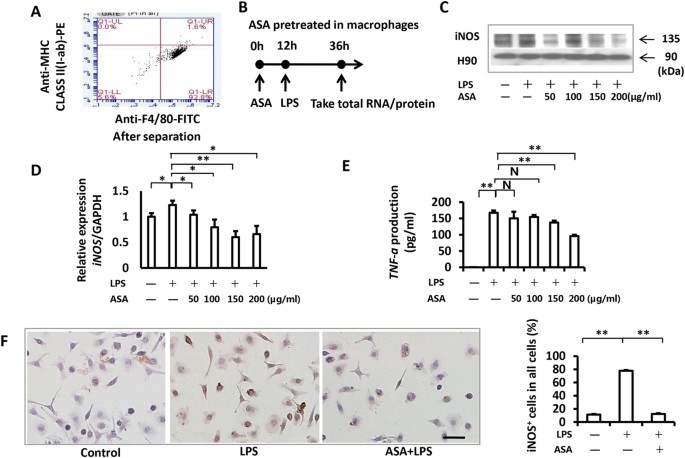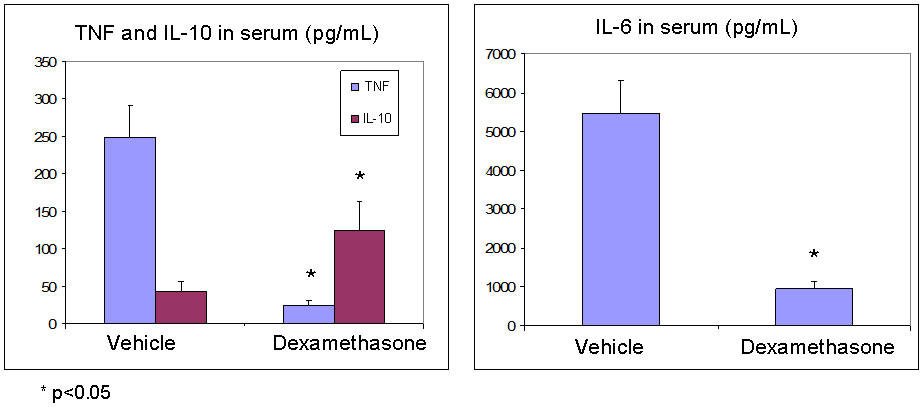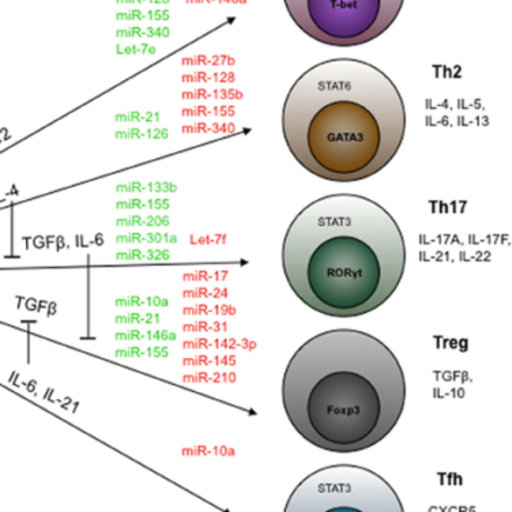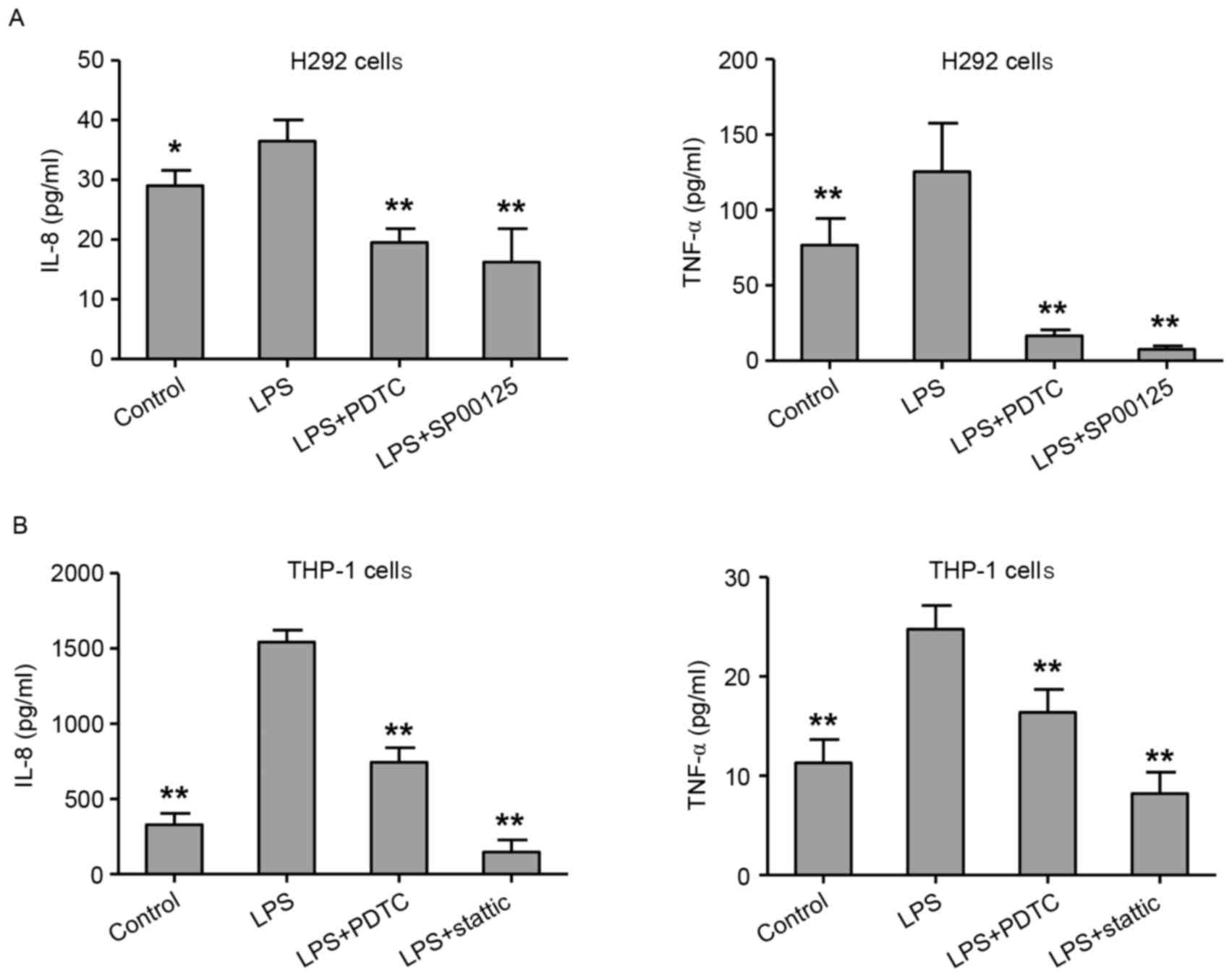
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Steps of ovarian stimulation with DuoStim protocol. Gn = Gonadotrophin,... | Download Scientific Diagram
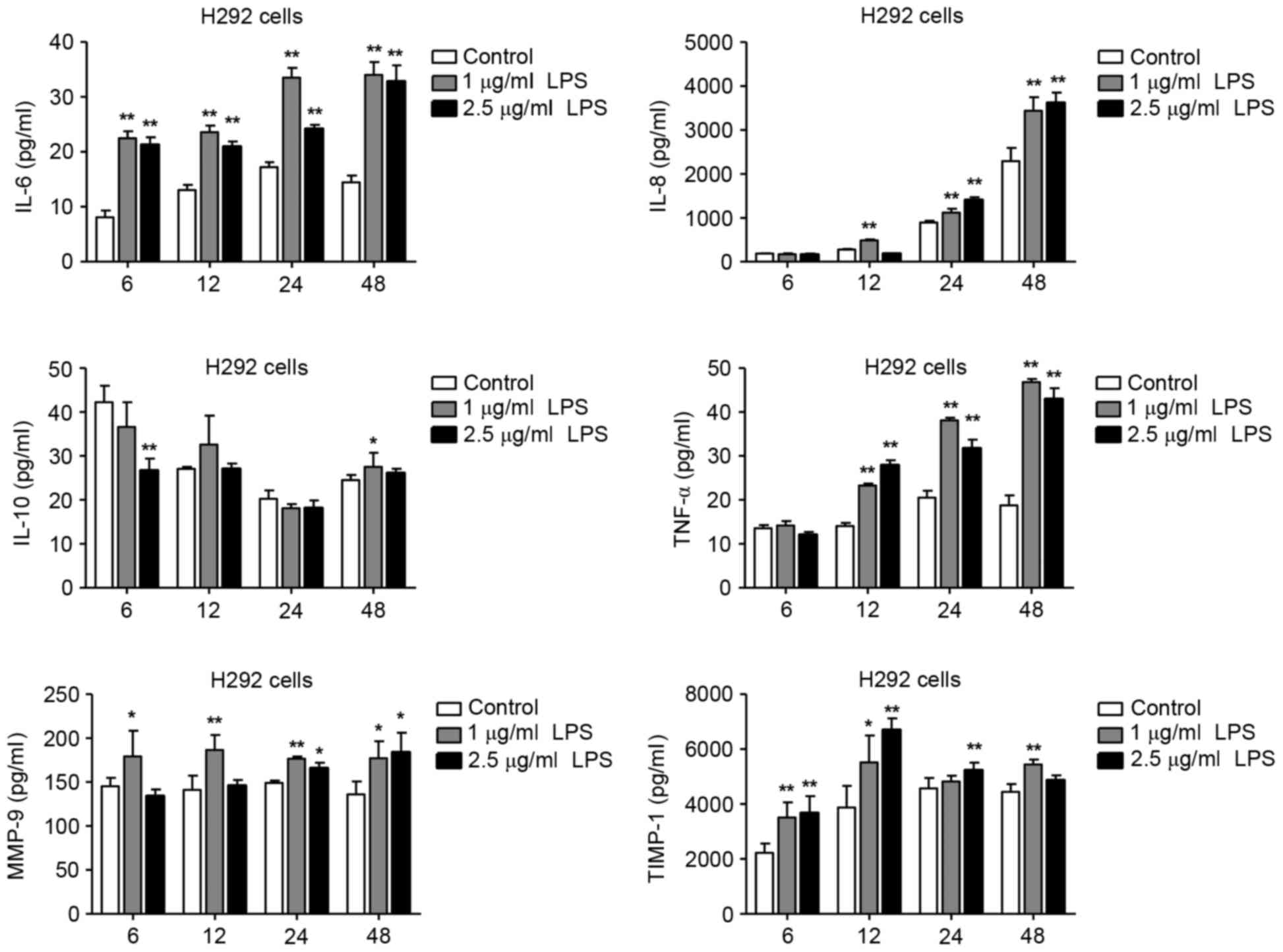
LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation

Repolarization of M(IFNγ+LPS) to M(LPS+IC). (A,B) The protocol used... | Download Scientific Diagram
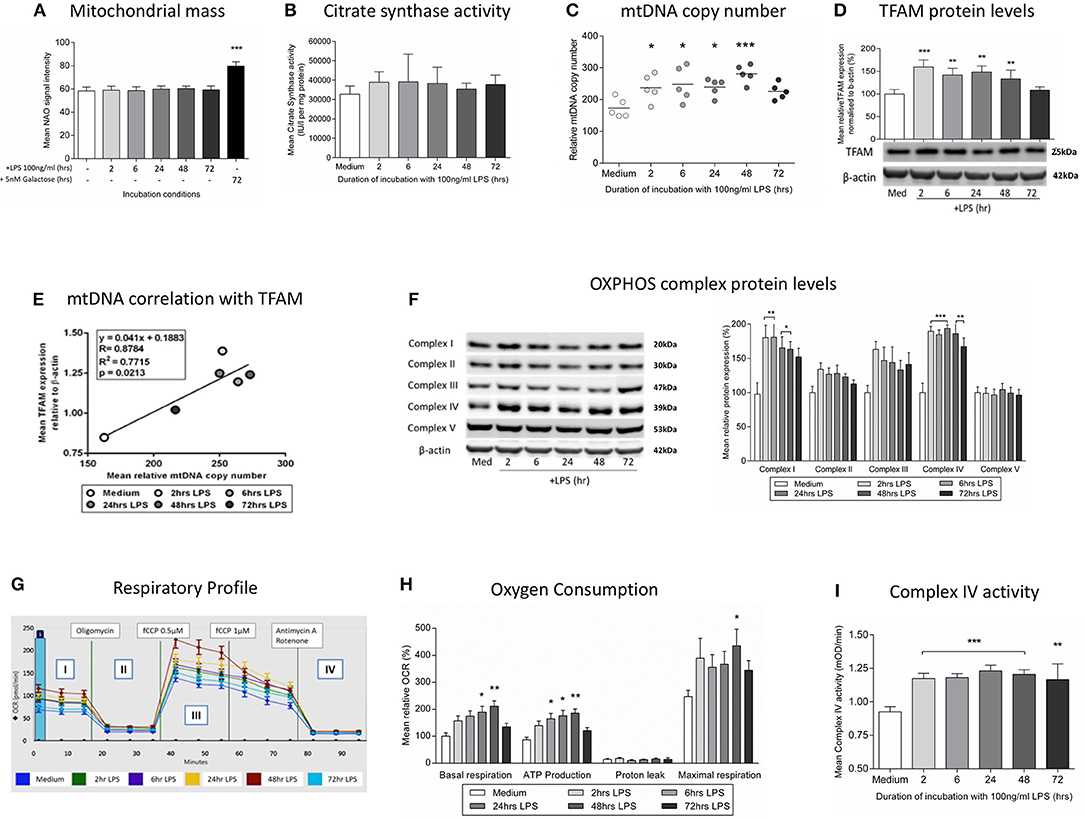
Frontiers | Exposure of Monocytic Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Induces Coordinated Endotoxin Tolerance, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Mitophagy, and Antioxidant Defenses

Evidence for the Modulation of the Immune Response in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells after Stimulation with a High Molecular Weight β-glucan Isolated from Lactobacillus fermentum Lf2 | bioRxiv
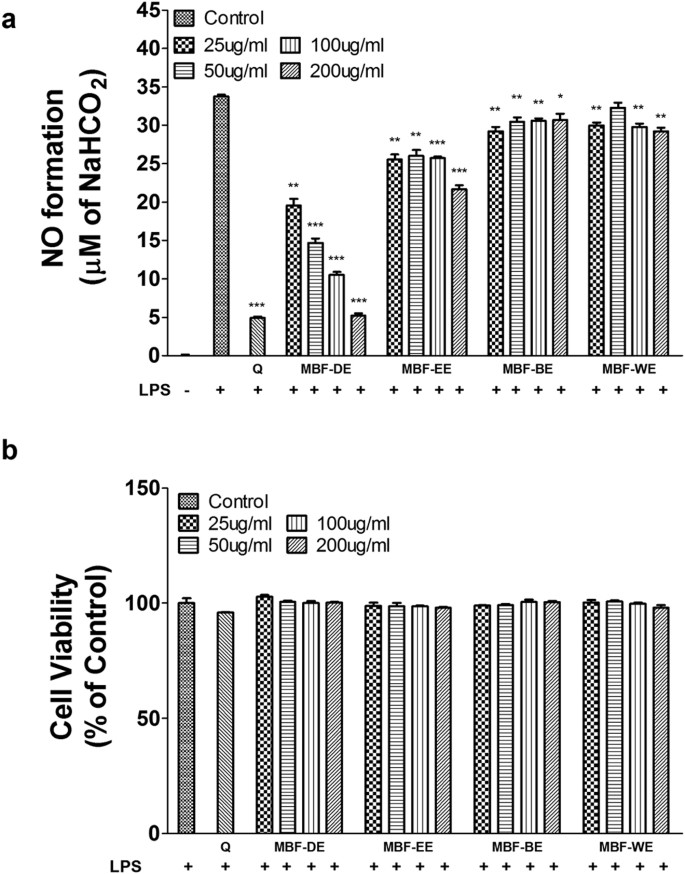
Mulberry fruit prevents LPS-induced NF-κB/pERK/MAPK signals in macrophages and suppresses acute colitis and colorectal tumorigenesis in mice | Scientific Reports
Lipopolysaccharide-driven Th2 Cytokine Production in Macrophages Is Regulated by Both MyD88 and TRAM*
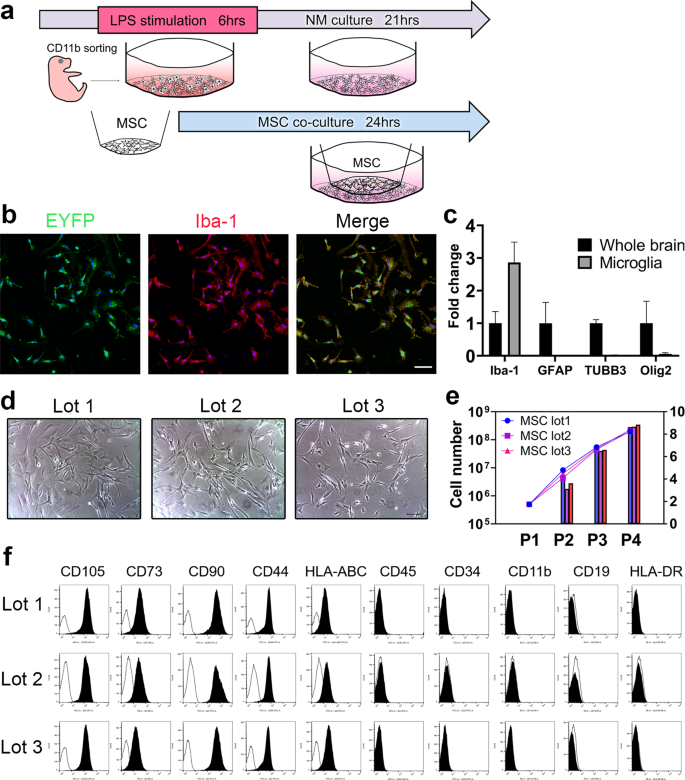
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells immunomodulate and restore actin dynamics and phagocytosis of LPS-activated microglia via PI3K/Akt/Rho GTPase pathway | Cell Death Discovery

Standardized protocols for differentiation of THP-1 cells to macrophages with distinct M(IFNγ+LPS), M(IL-4) and M(IL-10) phenotypes - ScienceDirect
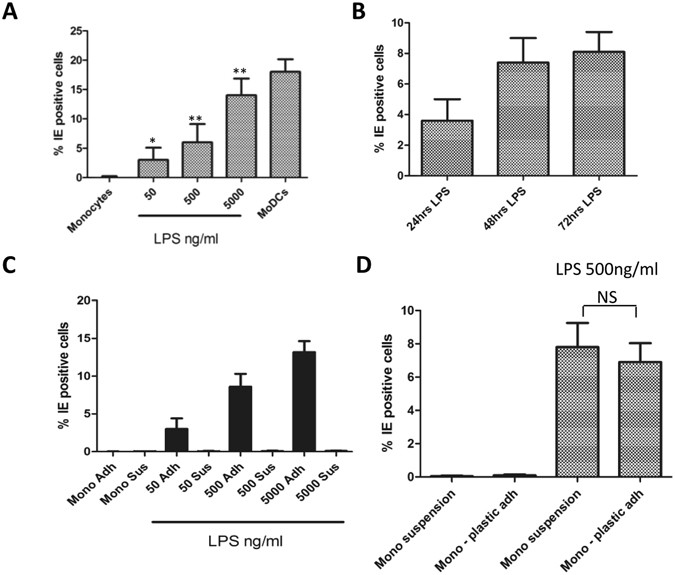
LPS promotes a monocyte phenotype permissive for human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene expression upon infection but not reactivation from latency | Scientific Reports
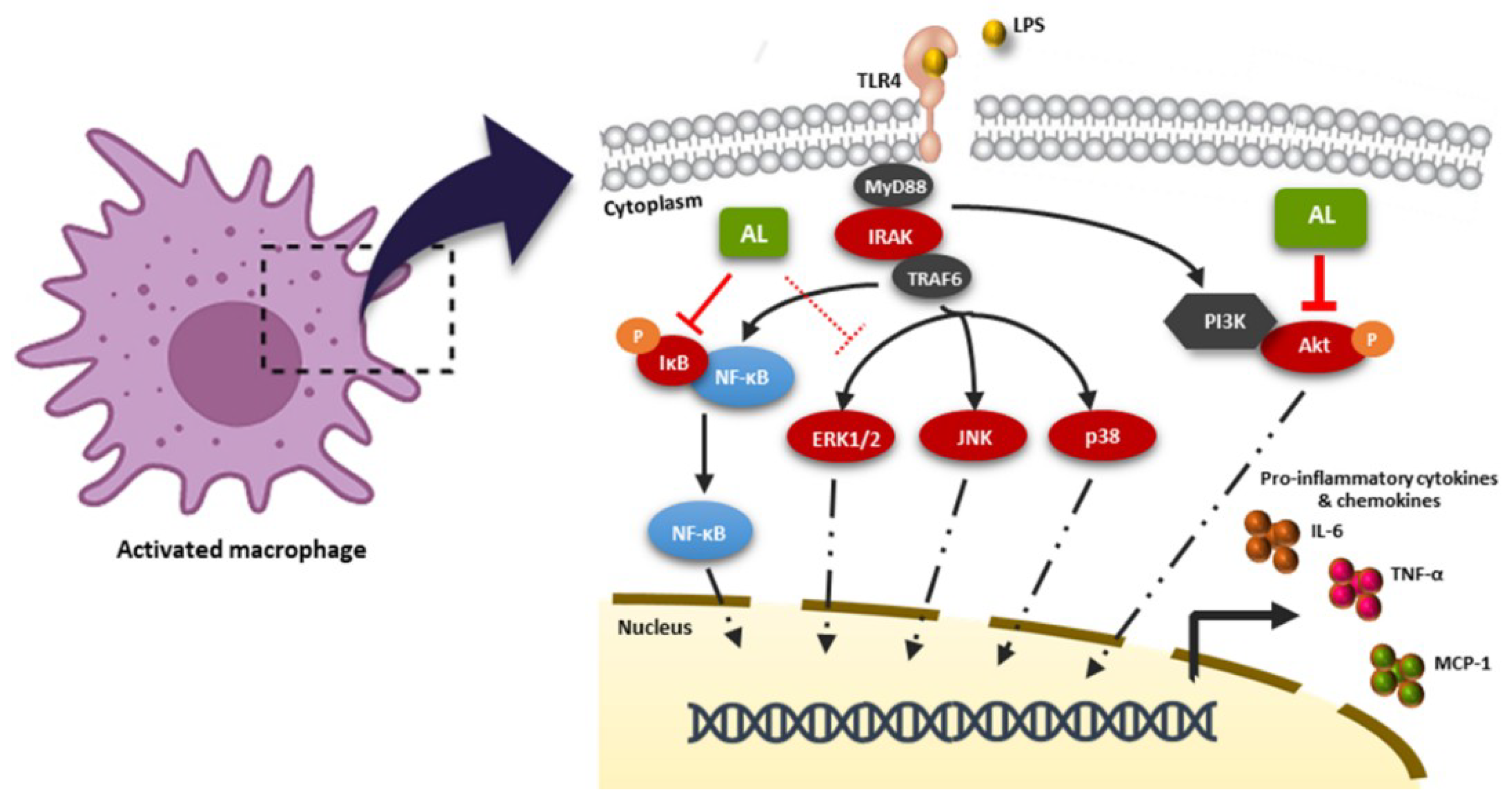
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Artocarpus lakoocha Extract Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells
Lipopolysaccharide-driven Th2 Cytokine Production in Macrophages Is Regulated by Both MyD88 and TRAM*
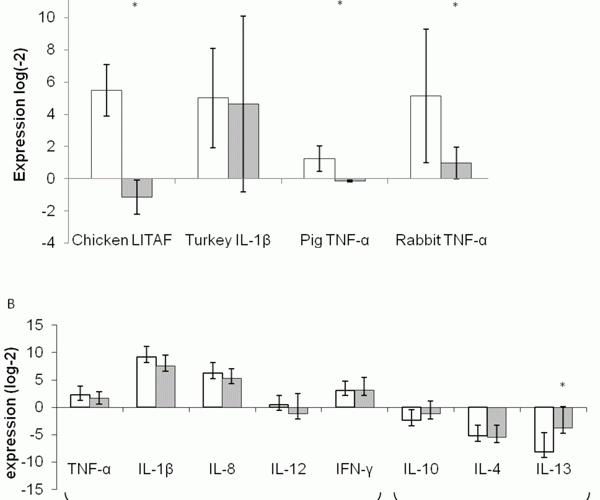
Ex-vivo LPS stimulation model coupled with quantitative PCR and its multispecies application in immunonutrition - European Pharmaceutical Review

LPS stimulation of PBMC suppresses SEB-induced cytokine production in T... | Download Scientific Diagram

Frontiers | Exposure of Monocytic Cells to Lipopolysaccharide Induces Coordinated Endotoxin Tolerance, Mitochondrial Biogenesis, Mitophagy, and Antioxidant Defenses

LPS‑induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF‑κB, STAT3 or AP‑1 activation
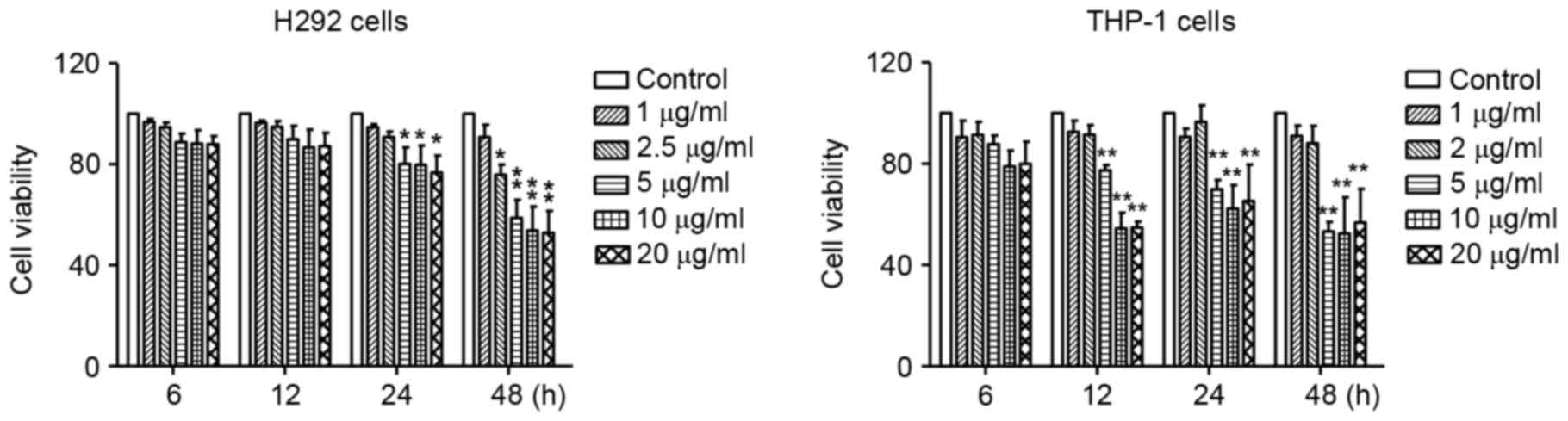
.jpg)